| Introduction |
Basic Conceptions
| First-Order Differential Equations |
Directly Integrable Equations
Motion of a Body - Problem 1
Motion of a Body - Problem 2
Motion of a Body - Problem 3
The Spontaneous Radioactive of Substance
Separable Equations
Motion of Particals in Viscous Fluid
Newton's Model of Cooling
Model of Population
Separable Equations
Motion of Particals in Viscous Fluid
Newton's Model of Cooling
Model of Population
Homogeneous Equations
Linear Equations
Bernoulli Equations
Exact Differential Equations
| Differential Equations of Higher Orders |
Basic Conceptions
Equations of Special Kinds
Some Graphic Illustrations using MATLAB
| Real-Life Problems:
Model of Population |
There exist experimental grounds that the rate of change of population is described by the following mathematical model,
![]() .
.
![]() ,
,
Let us transform the denominator of the integrand by making use of Partial Fractions Decomposition:
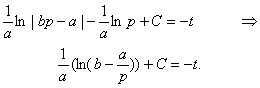
By making use of the initial condition p(0) = p0 we find the value of the integration constant:
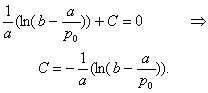
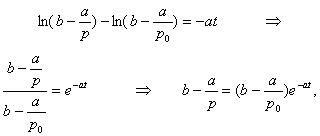
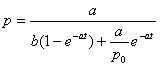
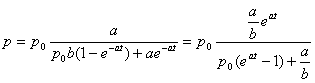
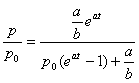 .
.
p(0) = p0
and
|
|