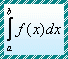| Introduction |
Basic Conceptions
| First-Order Differential Equations |
Directly Integrable Equations
Motion of a Body - Problem 1
Motion of a Body - Problem 2
Motion of a Body - Problem 3
The Spontaneous Radioactive of Substance
Separable Equations
Motion of Particals in Viscous Fluid
Newton's Model of Cooling
Model of Population
Homogeneous Equations
Linear Equations
Bernoulli Equations
Exact Differential Equations
| Differential Equations of Higher Orders |
Basic Conceptions
Equations of Special Kinds
Some Graphic Illustrations using MATLAB
| Homogeneous Equations |
A homogeneous differential equation can be represented by the following form:
![]() .
.
The right-hand side of the equation suggests the substitution
![]() ,
,
which implies
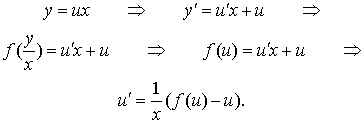
The latest equation is a separable equation.
Therefore,
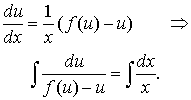
|
|