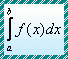| Basic Conceptions |
Primitives and Indefinite Integrals
Properties of Integrals
| Properties: Explanatory Comments |
Transformation of a Table of Common Derivatives to a Table of Integrals
A Table of Common Integrals
| Integration |
Techniques of Integration
| Integration by Substitution | ||
| ||
|
Integration by Parts |
| Integration of Rational Functions |
Basic Conceptions
Integration of Partial Fractions
Partial Fraction Decomposition
| Integration of Irrational Expressions |
Integrals Involving Rational Exponents
Integrals Involving Radicals
| Summary |
Extended List of Common Integrals
| Properties of Integrals |
| Key Topics Remaining: Table of Common Integrals » Techniques of Integration » Integration of Rational Functions » Integrals Involving Rational Exponents » Extended List of Common Integrals |
1. Differentiation is the inverse operation of integration:
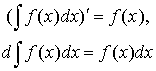
Note that symbols d and 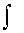 cancel each other if they follow
one after another.
cancel each other if they follow
one after another.
2. Integration of the derivative of f (x) yields the function f (x),
![]() .
.
3. A constant factor can be taken out the integral sign,
![]() .
.
4. The integral of an algebraic sum of functions equals the algebraic sum of the integrals of the functions,
![]() .
.
![]()
for any differentiable function u = u(x).
|
|