
 |
| Discrete Algebra |

Sigma-Notations Arithmetic Progressions Geometric Progressions Binomial Theorem Pascal's Triangle
1 + 2 + ... + n 1² + 2² + ... + n² 1³ + 2³ + ... + n³
Basic Conceptions Constituents of the Induction Principle Model Examples Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 |
Problem. Prove by
induction the statement Pn
:
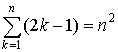
Proof.
|