| |
||||
| Numbers and Sets |

About Algebra
Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Criterions for Divisibility
Geometric Interpretation of Real Numbers Irrational Number Properties of Real Numbers Proportions Property of Equal Proportions Graphical Illustrations
Subsets Operations with Sets Intervals |
Intervals are special subsets
of the set of real numbers. Open interval (a,
b) is the set of points x An open interval of the form (a – δ, a + δ) is called a δ–vicinity of the point a. It is shown in the figure below. 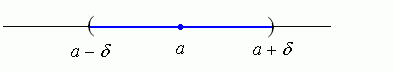
A half-open interval contains all points between the endpoints and one of the endpoints. Half-open interval [a,
b) is the set of points x
Half-open interval (a,
b] is the set of points x An interval is called closed if both endpoints are included in the interval. Closed interval [a,
b] is the set of points x An infinite interval is
the set of all real numbers. It has no endpoints and so infinity symbols
are enclosed by round brackets, A half-infinite interval
is a set of real numbers represented by a part of the number line bounded
from one side and unbounded from the other, in the direction of positive
or negative infinity.
|