
About Algebra

Addition and Subtraction

Multiplication
and Division

Criterions for Divisibility

 Types of Numbers Types of Numbers

Geometric Interpretation of Real Numbers

Irrational Number 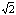

Properties of Real Numbers

 Fractions Fractions
Proportions

Property of Equal Proportions

 Absolute Values Absolute Values

Graphical Illustrations

 Sets Sets

Subsets

Operations with Sets

Intervals
|

|

|
An even number is divisible by 2.
A number is divisible by 3 if it is formed of digits, the sum of which is a number divisible by 3.
A number is divisible by 4 if its two last digits form a number, which
is divisible by 4.
A number is divisible by 5 if its the last digit is zero or 5.
A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by 2 and by 3 at the same time.
A multidigit integer is divisible by 8 if its three last digits form
a number, which is divisible by 8.
A number is divisible by 9 if it is formed of digits, the sum of which is a number divisible by 9.
A number is divisible by 10 if its the last digit is zero.
A multidigit integer is divisible by 25 if its two last digits form
a number, which is divisible by 25.
A number is divisible by 100 if its two last digits are zeros.
|
